Hijama, also known as wet cupping, is an ancient alternative therapy that has been used
for centuries in various cultures around the world. It involves placing cups on the skin and
creating a vacuum to draw blood from the body to promote healing and improve overall
health. However, like any other medical or therapeutic procedure, there are certain
precautions and guidelines that need to be followed to ensure safety and effectiveness. In
this blog, we will explore everything you need to avoid with hijama or wet cupping.
When Should You Avoid Hijama or Wet Cupping?
Avoid Hijama While Fasting
1. Dehydration: Fasting already leads to a reduction in bodily fluids, and Hijama or Wet
Cupping can further dehydrate the body, leading to weakness, dizziness and other
complications which might require the person to break their fast
2. Low Blood Sugar: During fasting, blood sugar levels drop, and Hijama can cause a
sudden drop in blood sugar levels, leading to hypoglycemia.
3. Loss of Nutrients: During fasting, the body relies on stored nutrients for energy, and
Hijama can result in further loss of nutrients, leading to weakness and fatigue.
4. Infection: Hijama involves creating small incisions on the skin, which can increase the
risk of infection. This risk is higher during fasting as the body’s immune system may be weakened.
Avoid Hijama if You Have These Conditions
Bleeding Disorders: Hijama/Wet cupping can be life-threatening to patients with
bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, Von Willebrand disease, or other clotting
disorders.
Skin Infections: If you have any active skin infections that are fungal, viral or bacterial, it
is highly recommended that Wet cupping is not performed. This is due to the procedure
possibly spreading to other body parts.
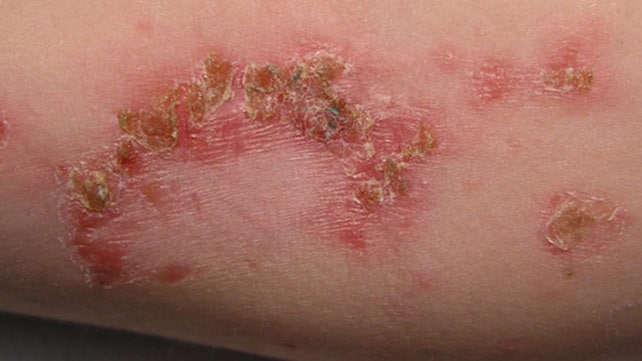
Skin conditions: If you have a skin condition such as eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea, it
is advisable to avoid Hijama or wet cupping. The procedure can exacerbate the condition
or cause further damage to the skin.
Chronic illnesses: People with chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, low
blood pressure, Hepatitis, Meningitis, Tuberculosis or late-stage Cancer should be
cautious about Hijama or wet cupping therapy. The procedure may worsen their condition
or cause complications, possibly leading to death.
Immunocompromised: Individuals who are immunocompromised due to medication,
medical treatment, or medical conditions such as HIV or cancer are at a higher risk of
infection after the procedure.
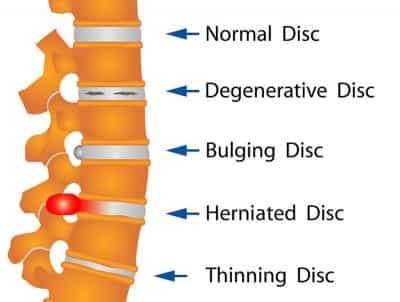
Spine/Disc Issue: Caution must be exercised when treating patients experiencing back
pain. It is essential to rule out any spinal disc issues before administering Hijama therapy,
as placing a cup on the affected area and applying suction may aggravate the condition if
there is any damage to the spinal disc. Therefore, patients with back pain should consult
their GP/Doctor to obtain appropriate advice on the suitable treatment course. It is also
highly recommended to perform Hijama with a health professional, such as a
physiotherapist or chiropractor, who will position cups in the most optimal position to help
aid and recover disc/spine issues.
Medication: Some medications may interact with Hijama/wet cupping or increase the
risk of bleeding. If you are taking medications such as blood thinners, anticoagulants, or
aspirin, it is advisable to avoid Hijama/wet cupping.
Allergies: Individuals who are allergic to the materials used in Hijama/wet cupping, such
as the plastic suction cups, antiseptic or the stainless steel blade, should avoid the
procedure.
What Should I Avoid Before Hijama or Wet Cupping?
- Diet and Beverages
Eating a heavy meal: It is recommended to have a light meal or fast for a few hours
before the procedure, as having a heavy meal can cause discomfort and nausea during
the process.
Drinking caffeine or alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can increase blood pressure and
make the skin more sensitive, making the procedure more painful and increasing the risk
of complications.
Consuming high-fat or fried foods: Consuming high-fat or fried foods can increase
blood viscosity and make the procedure more painful.

- Medications
Taking blood thinners: If you take blood-thinning medication such as aspirin or warfarin,
you should avoid Hijama, as these medications can increase the risk of excessive bleeding.
Taking medication that affects blood sugar levels: If you are taking medication for
diabetes or insulin, you should consult your GP first before undertaking Hijama.
- Physical Activities
Exercising Vigorously: Avoid strenuous exercise before treatment as it can cause
dehydration.

Exposure to extreme temperatures: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures such as
saunas, hot baths, or ice baths as it can affect blood circulation and increase the risk of
complications
- Mental and emotional state
Stressful Activities: Avoid any activities that may cause stress as it can spike up your blood pressure, making the procedure more painful
Anxiety and fear: It is essential to remain calm and relaxed before the procedure, as anxiety and fear can increase blood pressure and make the procedure more painful.
What should I avoid after Hijama or Wet Cupping?
- Physical activities to avoid
Strenuous exercises such as heavy lifting, running, or jumping should be avoided after
hijama as they can stress your body after you have lost blood. You also don’t want to
sweat within 4 hours after the Hijama treatment to minimise any risk of infection.
- Clothing to wear after Hijama
Wearing tight clothing can restrict blood flow to the affected area and delay the healing
process. It’s best to wear loose and comfortable clothing that allows your skin to breathe.
- Beverages to avoid
Caffeine can cause dehydration and slow down the healing process. It’s best to avoid
these beverages for at least 24 hours after hijama.
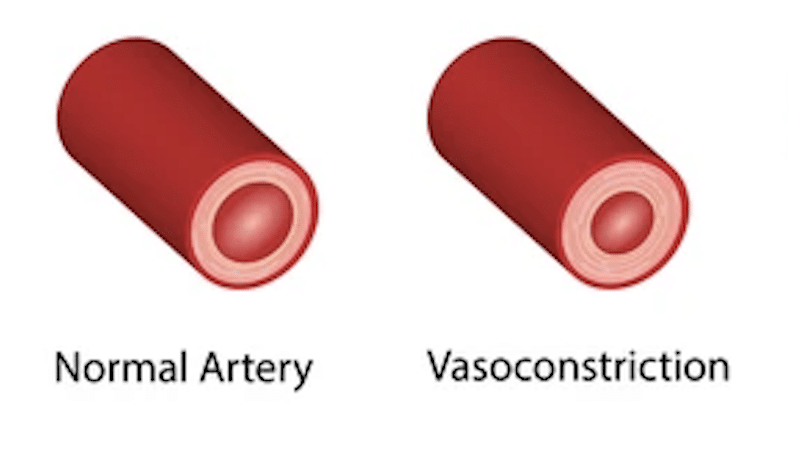
- Smoking
Smoking can cause vasoconstriction, decreasing blood flow to the affected area and
slowing the healing. It’s best to avoid smoking for at least 24 hours after hijama.
- Diet to follow post Hijama
Eating heavy meals after hijama can cause indigestion and slow down the healing
process. Instead, opt for light and nutritious meals that are easy to digest (examples of
food that are harder to digest; red meats)
- Exposure to sun
Exposure to the sun can cause the skin to become irritated and slow down the healing
process. It’s best to avoid exposing the affected area to the sun for at least 24 hours after
hijama.
- Hygiene practises after Hijama
It’s important to keep the affected area clean and dry to prevent infection. Avoid using
harsh soaps or rubbing the area vigorously when cleaning it.
- Follow-up care and consultation
Always follow up with the practitioner after hijama and inform them of any symptoms or
concerns. They may recommend further treatments or suggest modifications to your
lifestyle or diet.
- Physiotherapy or massage on the cupped areas
It is generally not recommended to have physiotherapy or massage immediately after wet
cupping, mainly where the cups were applied. This is because the skin and underlying
tissues may be sensitive and tender, and applying pressure or friction to the area could
cause discomfort.
It is advisable to wait at least five days after wet cupping before having a massage or any
other form of bodywork in the same area. During this time, keeping the area clean and
avoiding exposure to excessive heat or cold is important.
Where to Avoid Doing Hijama or Wet Cupping on the Body?
Eyes: Wet cupping or hijama should never be performed near the eyes or on the face
due to the risk of injury to the eyes or surrounding structures.
Genitalia: Wet cupping or hijama should also be avoided in the genital area due to the
sensitivity of the area and the potential risk of infection.
Major blood vessels: Areas where major blood vessels are located, such as the neck,
chest, or abdomen, should be avoided during wet cupping or hijama. The risk of bleeding
or injury to these blood vessels is high and could lead to severe complications.
The inner elbows, armpits, and backs of the knees: These areas can be sweaty, and
the skin folds in this region which can affect the skin healing process and increase the
risk of infection.
Fronts of the wrists: The veins in these areas are very close to the surface of the skin
and should be avoided. Remember, in Hijama, we NEVER cup veins.
Bony prominences: Wet cupping or hijama should not be performed over bony
prominences such as the spine, hip bones, or shoulder blades. These areas are more
sensitive and can cause discomfort or injury.
What Is the Minimum Age From When You Can Do
Hijama or Wet Cupping?
Parents of children under 16 years old should notify their GP/doctor and have it
documented in their medical records if they plan to try an alternative therapy, such as
Hijama. It is recommended that Hijama is not performed on children as young as 4-5
years old unless there is a compelling need or no other viable alternatives.
Can Pregnant Women Be Cupped?
Depending on the stage of pregnancy, there is a risk of either miscarriage or premature
labour. If a woman experiences any discomfort, pain, or symptoms during pregnancy,
she should be recommended to explore other safe, natural remedies.

Can Hijama Be Done for Women in Their Periods?
Yes, it is safe for women to do Hijama while on their menses. There is no Islamic or
Medical prohibition unless a woman is experiencing a heavy menstrual period and is not
feeling well.
In conclusion, wet cupping or hijama can be a beneficial and effective therapy for various
health conditions when performed safely and correctly. However, awareness of this
treatment’s potential risks and pitfalls is crucial to ensure a positive outcome. By steering
clear of these mistakes, you can ensure a safe and effective wet cupping experience,
promoting your health and well-being.
Consult a qualified and experienced practitioner, follow proper hygiene protocols,
communicate openly with your practitioner, and adhere to aftercare instructions for
optimal results.
For more information about Hijama & Wet Cupping, check out:
- Our frequently asked questions: www.masnad.com.au/hijama-wet-cupping/
- Our Hijama Blogs: https://www.masnad.com.au/knowledge-centre/hijama-info-hub/
Our Sydney Bankstown Hijama therapists are skilled and experienced in treating athletes of all skill levels for optimum performance. Feel free to Book Online anytime or call us on (02) 9793 8840 today!