Osgood Schlatter’s disease is a condition which causes pain and swelling of the area below the knee which is known as the tibial tuberosity. This is where the tendon of the patella attaches itself to the tibia (the shin bone). This condition may also cause inflammation of the patellar tendon which stretches over the knee cap. It is a disease that affects the adolescents and young children who are experiencing growth. The muscles, tendons, bones and other various structures of these adolescents undergo rapid change. It occurs in children who are engaged in sports that involve jumping, a sudden change in movement and running such as basketball, soccer, and ballet.. This condition mostly heals itself over time and rest
Osgood Schlatter’s
What is it?
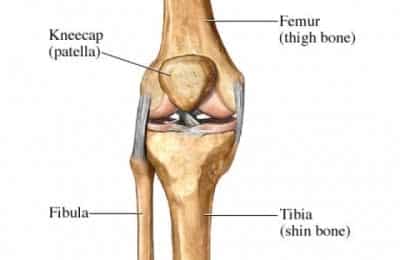
Causes Of The Osgood Schlatter’s
- Age – Osgood Schlatter’s affects children of both sexes. Commonly boys are affected between the age of 12 to 14 and girls from the age of 10 to 13. In rare cases, Osgood Schlatter’s can occur in adults. This usually happens if the disease was missed during the early developmental adolescent years.
- Activity – the condition is common in children who are engaged in sports that involve jumping, running and sudden changes in movement.
- Flexibility – when the quadriceps muscles are very tight they can increase the pulling of the tendons in the kneecap.
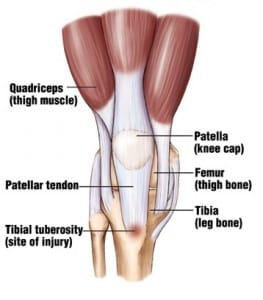
Symptoms Of Osgood Schlatter’s
- Experiencing knee pains due to the painful bump just below the knee.
- There is swelling or inflammation and can become worse with time.
- Pain is experienced during and after exercises.
- Weakness in the muscles of the front thigh can be experienced in chronic cases.
- Climbing stairs, kneeling and squatting can be very painful.
Diagnosis
When the doctor/physiotherapist is conducting the physical examination, he or she will look for redness, any swelling, tenderness and any knee pain around the knee. In rare cases, depending on the extent of the damage, an x-ray can be needed to examine the size of the damage to the knee joint.
Treatment
This condition usually resolves on its own over time and rest. At times the knee pains can be very severe, and one may need to take some medication for the knee pain treatment. You can buy some over the counter pain-relief to relieve the knee pains. Refer to your doctor if needed and follow their advice regarding pain-relief. A therapist can also guide you to do some physical exercises that stretch and strengthen the thigh’s quadriceps. This helps to reduce the tension in the tendons. Exercises that strengthen the knee tendons and the thighs can be used to stabilise your knee joints which should reduce the knee pains. A patella tendon strap can also be used to relieve the pressure. In very rare cases, surgery is recommended but is only done when the knee pain does not stop even after the growth spurts have ceased.
Tips And Tricks For Managing Daily Activities
- Icing The Injured Knee. This Helps To Reduce The Knee Pains And The Swelling.
- Resting The Injured Joint- You Should Reduce Your Movement To Reduce Irritation Of The Knee.
- During Sports, You Should Always Make Sure You Wears The Correct Protective Garments For The Knee. You should also follow a warmup and cool down protocol.
- Advised To Engage In low impact Activities That Do Not Involve Running Or Jumping, Such As Swimming.
Prevention
- Use The Osgood Schlatter’s Braces And Straps To Reduce The Impact Of Force When Jumping and changing direction.
- The Use Of Crutches at times may be Advised To Minimise Adding Too Much Weight On The Injured Knee.
- You Can Also Restrict Your Child From Engaging In Activities That Involve Jumping And Running.
How Long Till I Get Better?
Mild cases of Osgood Schlatter’s may take days to resolve, but for severe cases, the knee pains and swelling can take years to heal if left untreated or ignored. Therefore it is advisable to follow all prescribed treatments to ensure a quick recovery.

New Client Offer - 10% OFF
Are you in pain? Not sure if we can help you?
Book your initial appointment and receive 10% off any service!