Subacromial bursitis is inflammation of the fluid filled sac (bursa) that causes intense shoulder pain which worsens when moving the arm.
Subacromial Bursitis
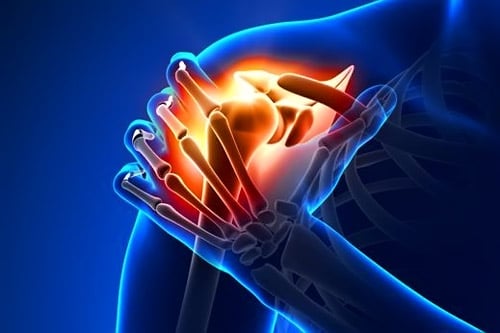
What is Subacromial Bursitis (SAB)?
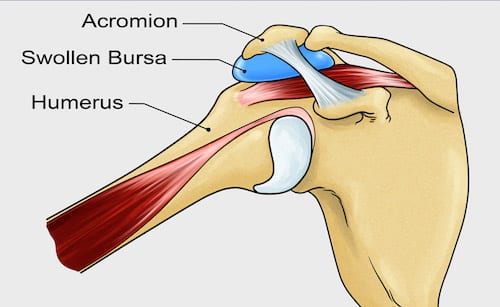
What Causes It?
Subacromial bursitis occurs when the bursa that sits between the shoulder bones, muscles and tendons swell and become inflamed. The inflammation can happen suddenly due to a shoulder injury or gradually due to overuse of the shoulder muscles.
People at risk of subacromial bursitis include:
Jobs involving repeated overhead lifting or forceful pulling.
Sports involving repeated throwing, pitching or swinging.
Symptoms
Here are some common signs that can point to subacromial bursa:
- Pain in the shoulder
- Shoulder stiffness
- Pain spreading down the arm towards the elbow or wrist
- Worse pain when reaching behind the head (washing hair) or lifting the arm above the shoulder (reaching for a shelf, swimming).
- Pain when lying on the shoulder, example when sleeping
- Redness or warmth on the shoulder
How is it diagnosed?
- Several questions will be asked about the shoulder pain (location, intensity, aggravators/relievers)
- A physiotherapist will do a few simple tests to see the strength and movement of the shoulder joint.
While the above steps can quickly diagnose subacromial bursitis, ultrasound or x-ray scanning may be performed to confirm.
Common Types of Bursitis
- Inflammatory bursitis is when the shoulder cushion becomes inflamed due to overuse.
- Calcified bursitis is when bone forms in the shoulder cushion due to chronic or recurrent bursitis.
- Septic bursitis is when there is an infection in the shoulder cushions.
Tips and tricks for managing daily activities
- First 1-2 weeks: avoid using the sore arm. Continue to use the opposite arms without increasing the pain.
- After 1-2 weeks: Start to use both arms without increasing the pain.
- Avoid activities that make the pain worse.
- Keep regularly used items at home or work below shoulder height.
- Sleep on the opposite shoulder.
Treatment
- Steroid injection
- Anti-inflammatory medication
- Education to manage pain and inflammation
- Soft tissue massage
- Joint mobilisation
- Simple exercises (stretches, strengthening) to avoid permanent stiffness and weakness
- Shoulder blade setting exercises to ensure correct shoulder positioning
How long until I get better?
The time of treatment may vary from patient to patient, but in most cases, the symptoms improve within a few months of treatment. Getting early treatment means you can avoid long-term joint problems.
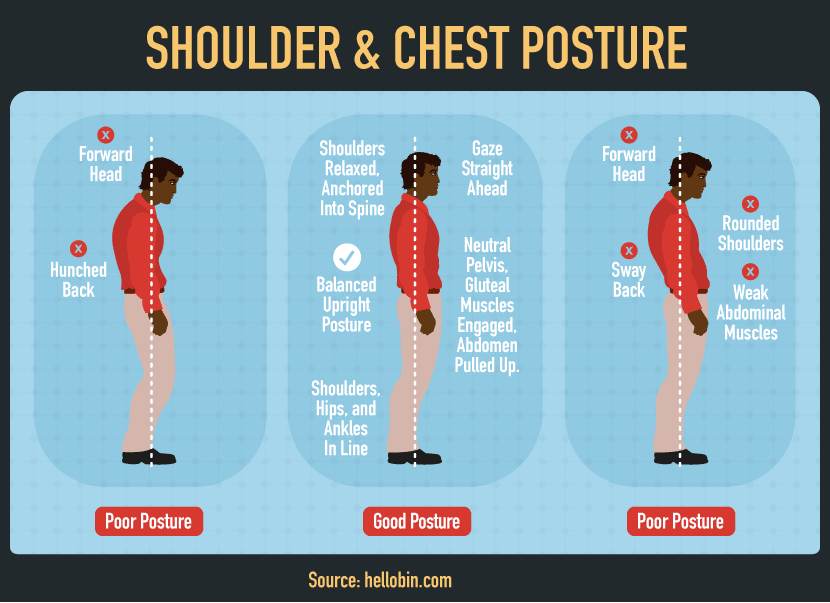
Take home message
- Subacromial bursitis is an inflammation that causes shoulder pain, usually gradually.
- At first, give time for the swelling and inflammation to go down before using the sore arm.
- Good posture can help to relieve symptoms.
- A physiotherapist can give exercises that will help with the symptoms and prevent permanent weakness and stiffness.
- Early treatment means permanent damage to the joint can be avoided.
For all your SAB needs, feel free to give us a call on 02 9793 8840 or Book Online

New Client Offer - 10% OFF
Are you in pain? Not sure if we can help you?
Book your initial appointment and receive 10% off any service!